Need for Data Sharing
For biomedical research, Clinical trials are essential components as they lay down the foundation for the researchers to investigate the significance of various treatments and interventions given to humans for disease cures.
The urgency for Clinical Trial Transparency is highlighted by the Declaration of Helsinki and the World Health Organization. It is rapidly making an appearance in the analytic domain of organizations, academicians, and the general public.
The listing of Clinical Trials on the public database has opened new avenues to check the operations inculcated by the drug manufacturing enterprise in obeying the regulation used for Good Clinical Practices. Clinical Trial Transparency also helps external scientific and medical investigators to collaborate with firms and strengthen the advantages to improve drug development for mankind’s well-being.
In spite of continuous efforts of authorities aimed at ensuring the following of regulation and clinical data transparency for all clinical trials, fewer than half of trials are published/disclosed in the public domain. In general, the absence of transparency can result in significant consequences for healthcare systems, patients, and medical practitioners.
The advantages of Data Transparency in Clinical Trials are listed as:
- The opportunity to reuse clinical data and documents (CSRs (Clinical Study Report)), which might speed up the development of drugs.
- Increased transparency could raise interest and awareness among trial participants and researchers.
- Transparency raises the scope to track the development of new treatments for unmet medical needs in our healthcare system.
- Additionally, it is possible to aggregate participant-level data from different trials to infer more than what can be derived from the results of a single trial.
- It tends to prevent sponsors from severe penalties imposed by regulatory bodies.
Needs and Scenarios on Clinical Data Disclosures
- EMA Policy 0070
- Health Canada PRCI
- EU CTR regulations
- Voluntary Data Sharing
- Registries such as CT.GOV etc.
Need for Data Anonymization
In contrast to Data Sharing needs there are data privacy regulations which binds the sponsor to make sure that personal data should not be shared. If shared, there shall not be any possibility of identifying individuals and their personal information from shared clinical data.
Clinical trial dataset contains personal and identifying information as mentioned below:
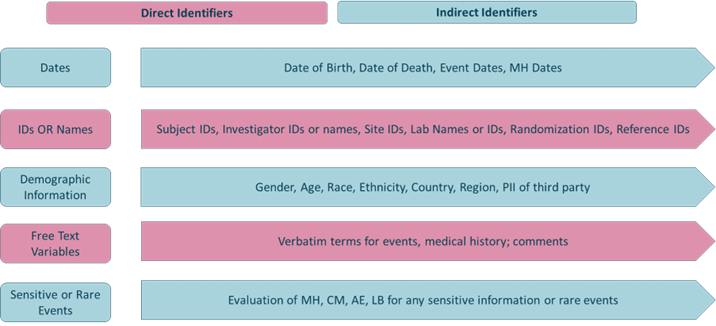
Direct Identifiers in dataset like Subject IDs, Investigator Name etc could lead to identification of subjects. This violates Data Protection Acts worldwide to protect personal information of individuals.
Quasi-identifiers are identifiers that by themselves do not identify a specific individual but can be aggregated and “linked” with other information to identify data subjects. For example, age, sex, race, adverse events etc.
This leads to need for anonymizing the clinical data so that there is no possibility to identify any individual. As ARTICLE 29 DATA PROTECTION PARTY states that data is anonymized if there is no possibility to single out an individual, link the information to identify and infer any information on particular individual with some probability above acceptable threshold:
- Singling out, which corresponds to the possibility to isolate some or all records which identify an individual in the dataset;
- Linkability, which is the ability to link, at least, two records concerning the same data subject or a group of data subjects (either in the same database or in two different databases). If an attacker can establish (e.g. by means of correlation analysis) that two records are assigned to a same group of individuals but cannot single out individuals in this group, the technique provides resistance against “singling out” but not against linkability;
- Inference, which is the possibility to deduce, with significant probability, the value of an attribute from the values of a set of other attributes
Identifying Identifiers and Anonymization Techniques
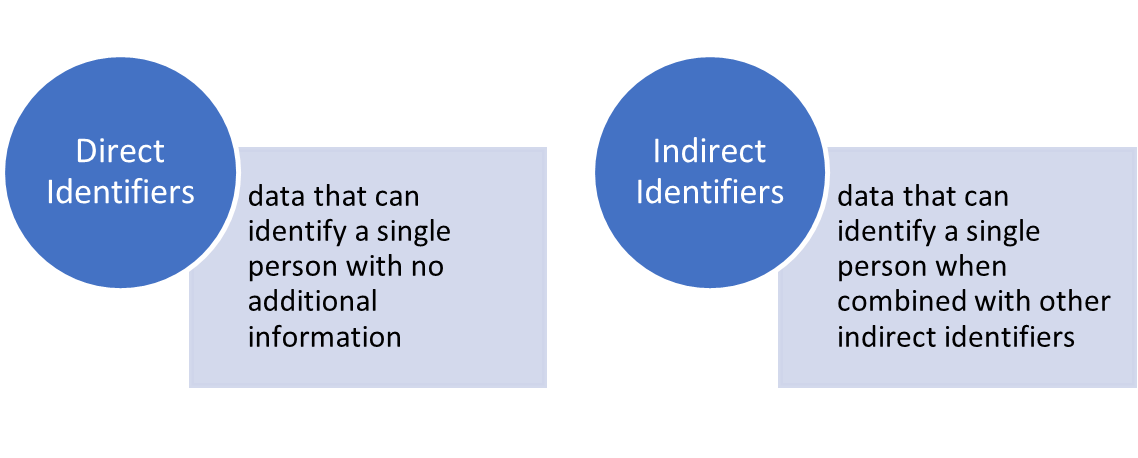
Identifiers are:
- Replicable (i.e. its values must be stable over time),
- Distinguishable (possess sufficient variation to distinguish it from other individuals in the data set), and
- Knowable (it must characterise information that an adversary can know and then use to re-identify the records in the data set)
Identifiers in Clinical Trial Data are:
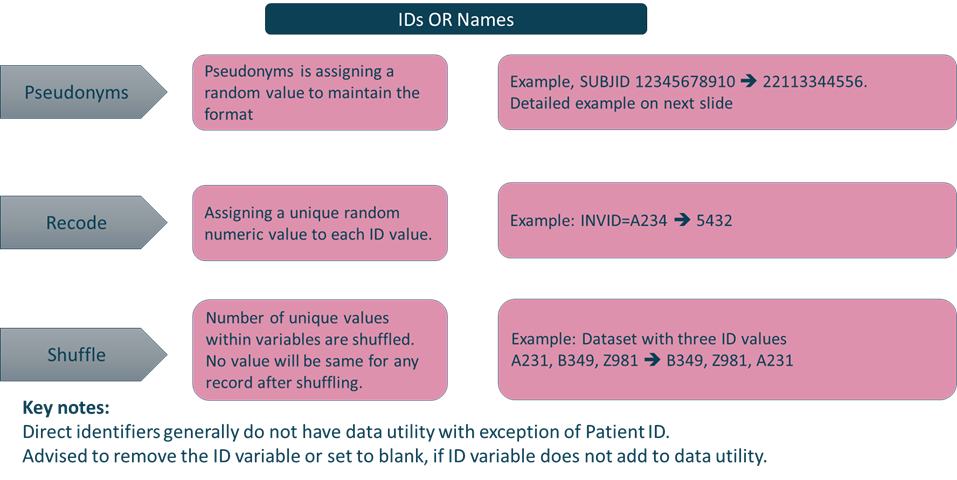
Anonymization Methods

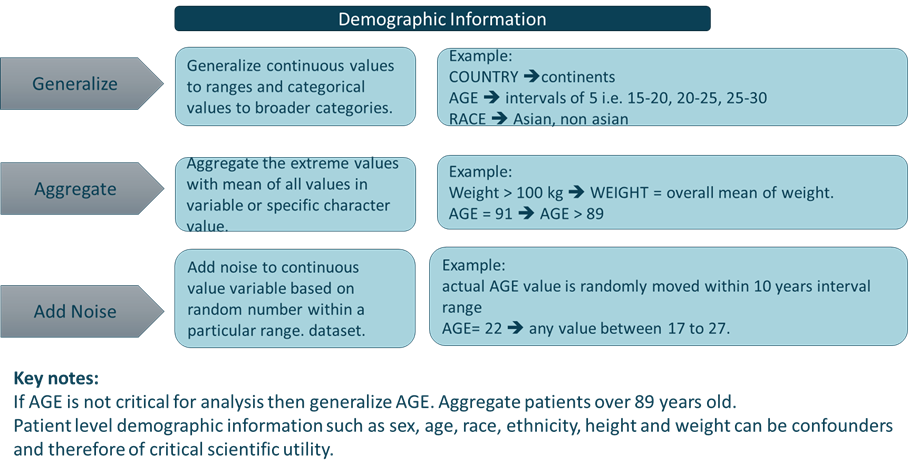
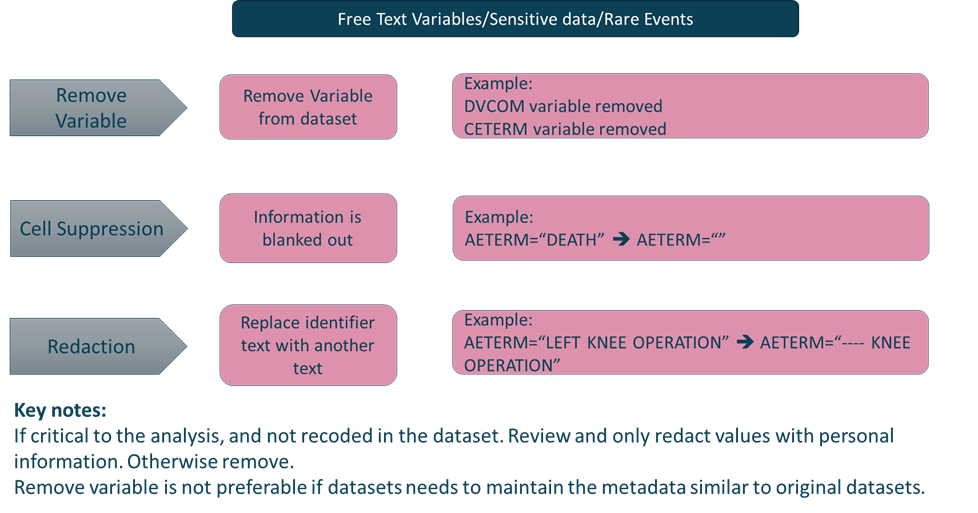
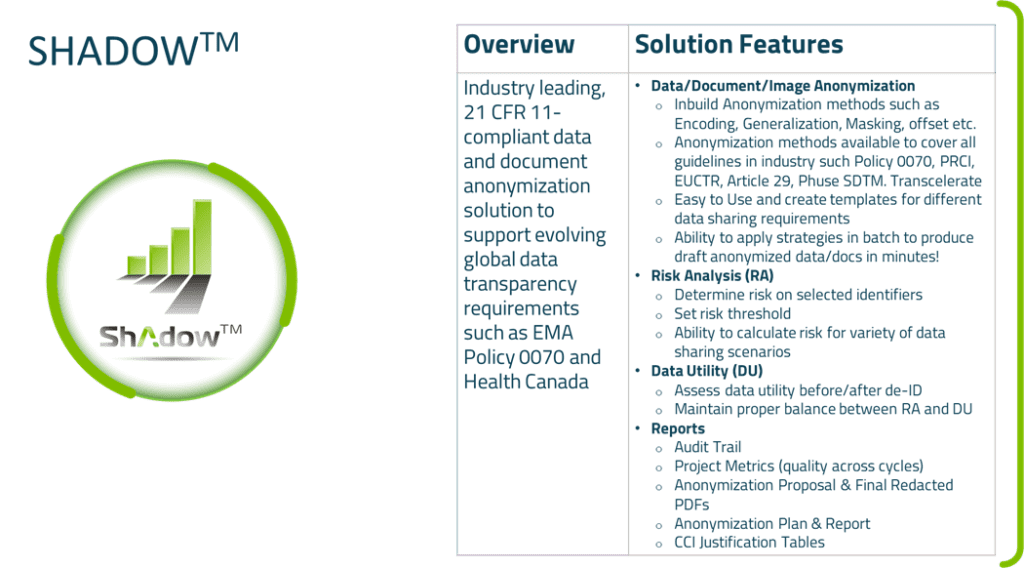
Need for Automation Tool
Anonymization of clinical data is not something which interests sponsor as it is not helping in their own research but for general public and researcher. But sponsors are responsible from the Data Privacy regulations perspective to protect the privacy of individuals involved in clinical trials.
Hence, sponsors need a robust tool to automate the process and minimize the risk of re-identification. Clinical Data includes structured and unstructured form of data. It needs an automation tool to anonymize clinical data uniformly for structured and unstructured forms.
GenInvo has developed an automation tool named Shadow™ (Data Anonymization Tool) which has all the required anonymization techniques available to anonymize clinical data.